How to Choose the Right Power Wire for Your Electrical Projects?
Choosing the right power wire is essential for any electrical project. Several factors play a significant role, including wire gauge and insulation type. According to industry standards, using the correct power wire can optimize performance and safety. A report by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association indicates that inappropriate wire choices account for 20% of electrical failures.
Different projects require different power wire specifications. For instance, residential wiring may differ from industrial applications. Understanding ampacity and voltage drop is crucial. A chart from the American Wire Gauge illustrates how wire size impacts both safety and efficiency. Factors such as environmental conditions also complicate choices.
Even experienced electricians face challenges in selecting power wire. Oversizing or undersizing can lead to significant issues. It's vital to assess each project's unique requirements. Seeking expert advice often proves beneficial. Striking a balance between cost and quality remains a common theme among professionals. Exploring various sources and materials can enhance decision-making.

Understanding the Basics of Power Wire Specifications
When embarking on electrical projects, understanding power wire specifications is crucial. The wire gauge determines the amount of current it can safely handle. Thicker wires, measured in lower gauge numbers, are better for high-power applications. For example, a 12-gauge wire can support more current than a 16-gauge wire. Inadequate wire thickness may lead to overheating, which could pose safety hazards.
Another essential specification is the wire’s insulation material. Different environments require different types of insulation. For outdoor use, look for wire rated for wet conditions. Indoor wiring may not need such robust insulation. Always check the temperature rating as well. Exceeding this can damage wires and affect performance. Many people overlook this detail. It's a mistake that can lead to project failure.
Voltage rating is also important. Ensure the wire can handle the voltage of your project. A mismatch could lead to short circuits. When in doubt, consult guidelines or experts. Ignoring wire specifications may seem trivial but can have serious consequences. Making informed choices leads to safer projects.
How to Choose the Right Power Wire for Your Electrical Projects?
| Specification | Description | Recommended Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Indicates the thickness of the wire; lower numbers mean thicker wire. | For high-current applications, lower AWG (e.g., 10-12 AWG). |
| Voltage Rating | Maximum voltage a wire can handle safely. | Use wire rated above your application voltage. |
| Insulation Type | Material that covers the wire for protection. | Consider environmental factors (heat, moisture). |
| Current Rating | Maximum current a wire can safely carry. | Choose based on load calculations. |
| Flexibility | How easily a wire can be bent or twisted. | Use stranded wire for applications needing flexibility. |
| Temperature Rating | Maximum temperature a wire can withstand. | Select based on installation environment (e.g., indoors, outdoors). |
Identifying the Appropriate Wire Gauge for Your Project
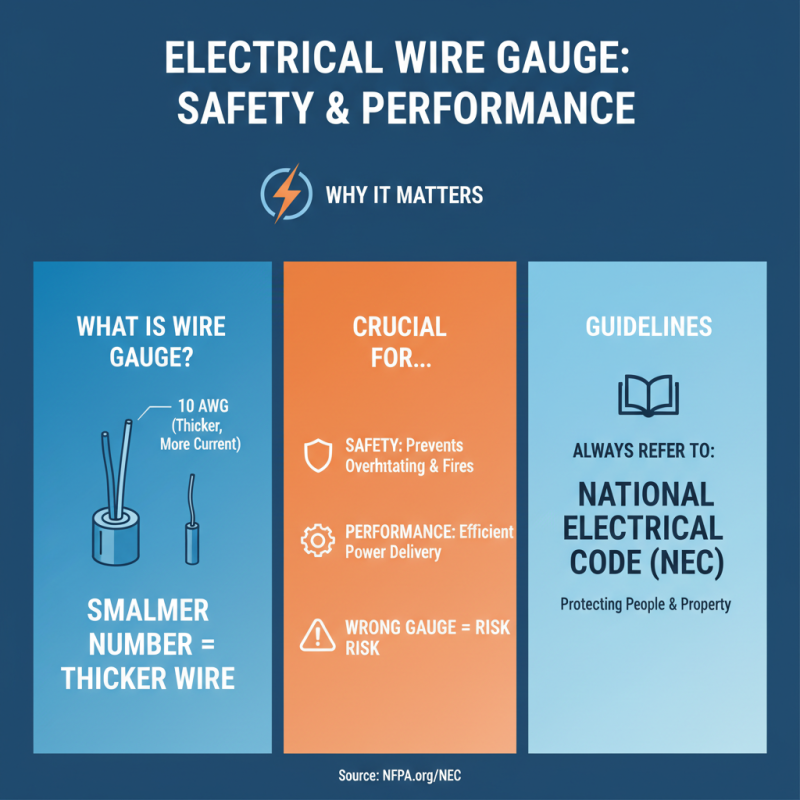
Choosing the right wire gauge is crucial for safety and performance in your electrical projects. The wire gauge indicates the thickness, which affects the amount of current it can carry. A smaller gauge number means a thicker wire, allowing it to handle more power. Always refer to the National Electrical Code (NEC) for guidelines.
When selecting wire gauge, consider the length of the run. Longer distances may need a thicker wire due to voltage drop. Know your project's current requirements. For example, a standard 15-amp circuit typically uses a 14-gauge wire. However, using a heavier gauge may be beneficial for larger loads.
Tips: Measure your wire runs accurately. An underestimate can lead to safety hazards. Check if the wire will be exposed to heat or moisture. This can affect its performance. Using the correct gauge isn't just about convenience; it's about reliability. Choosing the wrong gauge can lead to overheating and fire risks. Always double-check your calculations. Don't rush through this important step.
Evaluating Insulation Types for Different Applications
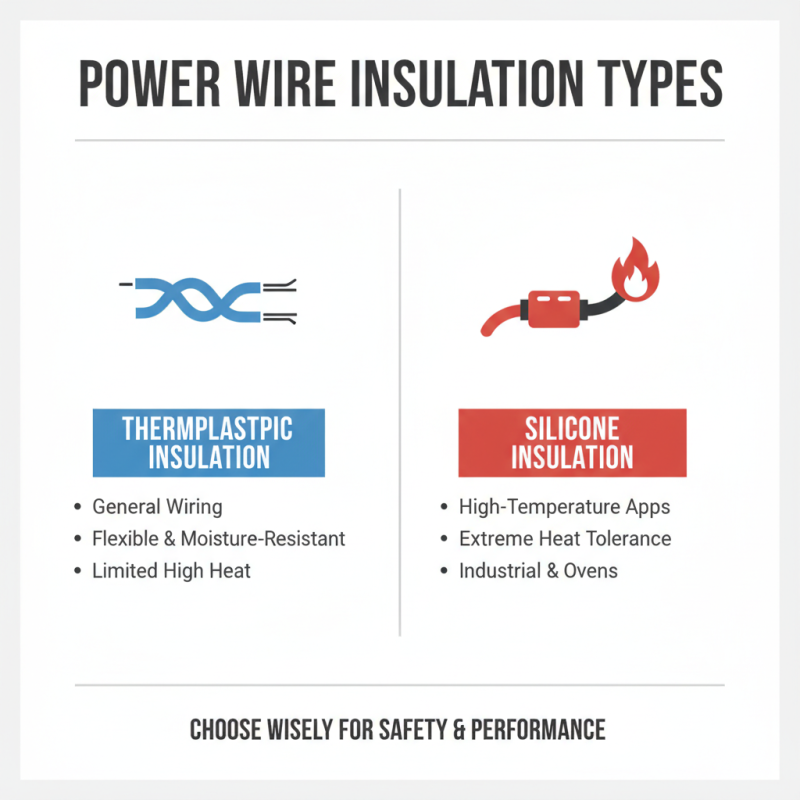
When selecting power wire for your electrical projects, insulation type plays a crucial role. Different applications require distinct materials. For example, thermoplastic insulation is commonly used for general wiring. It offers flexibility and resistance to moisture. However, it may not withstand high temperatures effectively.
Tips: Always check the temperature rating of the insulation. This ensures it meets your project's requirements.
Another option is rubber insulation. It is durable and provides excellent resistance to abrasion. This type is suitable for outdoor applications as it can endure various environmental conditions. Yet, it can be more expensive than other options. Think about your budget and project needs before deciding.
Tips: Consider both performance and cost during selection. This creates a balanced approach to your wiring needs.
With various insulation types available, evaluate your specific application carefully. Do not rush the decision. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each type will lead to better choices in your electrical projects. Always reflect on your requirements and potential challenges.
Considering Voltage Ratings and Current Carrying Capacity
When selecting power wire for electrical projects, understanding voltage ratings and current carrying capacity is crucial. The National Electrical Code (NEC) sets guidelines on these factors, helping ensure safety and efficiency. For instance, a wire rated for 600 volts can handle many residential applications. But if the voltage exceeds this limit, the risk of insulation failure increases. Using the wrong wire can lead to overheating, posing fire hazards.
Current carrying capacity also plays a significant role. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) standard provides a system to determine wire size and its capacity. For example, a 12 AWG wire typically supports up to 20 amps. However, continuous loads may require derating the capacity by 10%. This means that users need to carefully calculate the total load and choose the right wire size accordingly. It's not a simple task, and many overlook these critical aspects.
Misjudgments in wire selection can lead to performance issues. Many projects fail when the wire cannot handle the load, leading to inefficient power delivery. It's important to analyze environmental factors too. High temperatures can decrease wire capacity. Understanding these intricate details is necessary for successful electrical work. Many professionals don't fully grasp these nuances, resulting in costly mistakes.
Determining Environmental Factors Impacting Wire Selection
When choosing the right power wire for your projects, environmental factors play a crucial role. Temperature extremes can affect wire performance. For instance, in cold climates, wires may become brittle. In hot conditions, they might expand and become less effective. Understanding the temperature range is essential.
Moisture is another significant factor. If wires are exposed to humidity, they might corrode faster. This can lead to short circuits. Ensure wires are rated for moisture exposure. If you're working in wet areas, consider using waterproof insulation.
Additionally, consider the physical environment. Wires exposed to mechanical stress should have extra protection. This may include tough insulation or protective conduits. Think about pests, too; rodents can damage wires. Regular checks can help prevent hidden risks. These details matter. Reflect on them when planning your projects.
How to Choose the Right Power Wire for Your Electrical Projects?
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Welding Cable for Your Projects in 2025
-
What is Lead Wire and Its Applications in Various Industries?
-
2025 Guide to Choosing the Right Wire and Cable for Your Projects
-

2025 Top 10 Marine Cable Innovations Transforming Global Connectivity
-
How to Select the Right MC Cable for Your Electrical Projects
-

Maximizing Safety and Efficiency: The Essential Guide to Choosing Electrical Wire Connectors in 2023
